Introduction
In today’s digital age, the insurance industry heavily relies on data to underwrite policies, assess risks, and provide personalized services. While data-driven insights have revolutionized the industry, they also pose significant challenges in terms of data privacy and security. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, it is imperative for insurance companies to prioritize data protection and implement robust security measures.
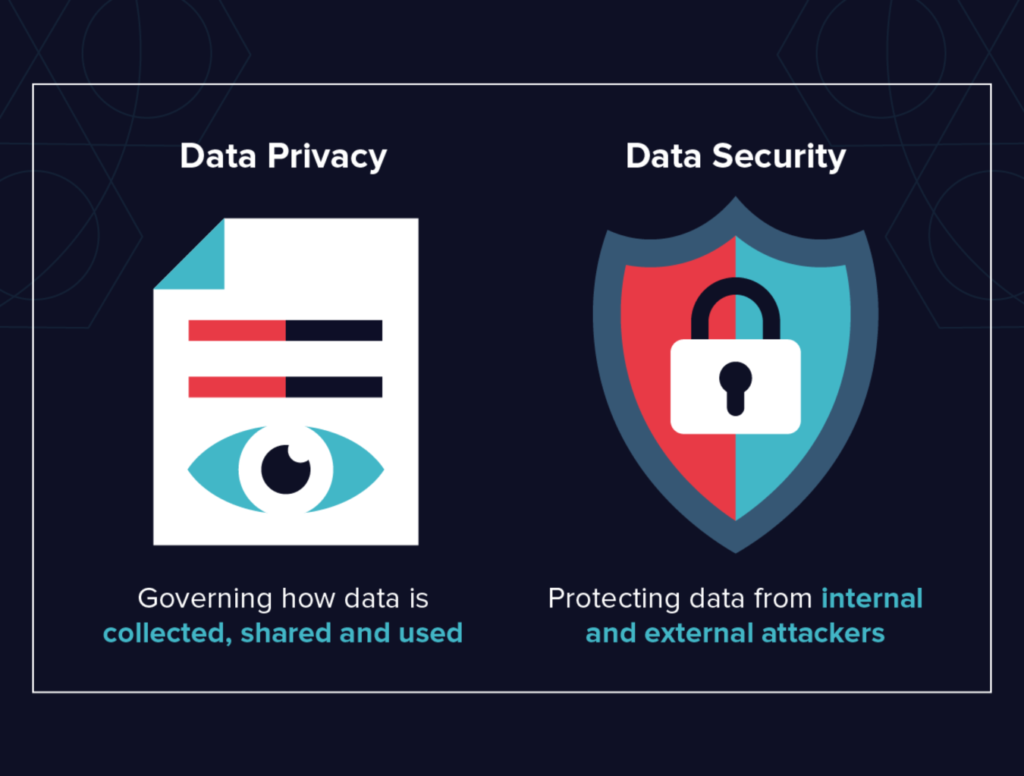
The Importance of Data Privacy in Insurance
Data privacy is fundamental to building trust between insurers and their customers. When customers share personal and sensitive information, they expect it to be handled responsibly and ethically. Breaches of data privacy can lead to severe consequences, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
- Customer Trust: Data privacy is essential for building and maintaining customer trust. When customers feel confident that their information is secure, they are more likely to choose an insurer and remain loyal.
- Regulatory Compliance: Insurance companies must adhere to stringent data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
- Risk Mitigation: Data breaches can expose insurers to significant financial and operational risks. By prioritizing data privacy, insurers can minimize the likelihood and impact of such incidents.
Key Data Privacy Challenges in the Insurance Industry
The insurance industry faces several unique data privacy challenges:

- Sensitive Personal Information: Insurers often handle highly sensitive personal information, including medical records, financial details, and family history.
- Third-Party Data Sharing: Insurers may share data with third-party vendors, such as claims processors or data analytics providers. This can increase the risk of data breaches.
- Cross-Border Data Transfers: Many insurers operate globally, which involves transferring data across borders. This raises concerns about data protection standards in different jurisdictions.
Strategies for Enhancing Data Privacy and Security
To address these challenges, insurers should adopt a comprehensive approach to data privacy and security:
- Strong Data Governance:
- Implement robust data governance policies and procedures.
- Assign clear data ownership and accountability.
- Conduct regular data audits and risk assessments.
- Advanced Security Technologies:
- Invest in advanced security technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Implement strong access controls and identity management practices.
- Regularly update and patch software to address vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training and Awareness:
- Provide regular training to employees on data privacy and security best practices.
- Promote a culture of security awareness and vigilance.
- Enforce strict security policies and procedures.
- Incident Response Planning:
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to address data breaches and other security incidents.
- Conduct regular simulations and drills to test the plan’s effectiveness.
- Have a clear communication strategy to inform stakeholders in case of a breach.
- Third-Party Risk Management:
- Conduct thorough due diligence on third-party vendors.
- Enforce strict data privacy and security requirements in contracts with vendors.
- Monitor the security practices of third-party providers.
- Privacy by Design:
- Incorporate privacy considerations into the design and development of new systems and applications.
- Minimize data collection and retention.
- Implement data minimization principles to limit the amount of data processed.
Conclusion
Data privacy and security are paramount for the insurance industry. By prioritizing these issues, insurers can protect their customers’ sensitive information, mitigate risks, and build long-lasting trust. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential for insurers to stay ahead of emerging threats and adopt innovative security solutions. By embracing a proactive approach to data privacy and security, insurers can safeguard their reputation, ensure compliance, and drive business growth.

